二叉树的最大路径和
LeetCode 124.二叉树的最大路径和
路径 被定义为一条从树中任意节点出发,沿父节点-子节点连接,达到任意节点的序列。同一个节点在一条路径序列中 至多出现一次 。该路径 至少包含一个 节点,且不一定经过根节点。
路径和 是路径中各节点值的总和。
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其 最大路径和 。
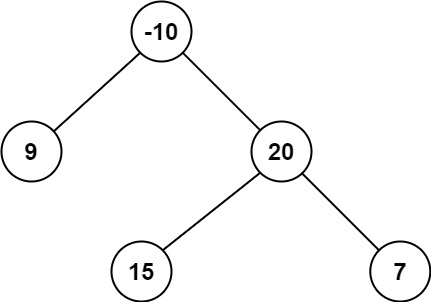
输入:root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:42
解释:最优路径是 15 -> 20 -> 7 ,路径和为 15 + 20 + 7 = 42
|
代码实现:
class Solution {
int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
maxGain(root);
return maxSum;
}
public int maxGain(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftGain = Math.max(maxGain(node.left), 0);
int rightGain = Math.max(maxGain(node.right), 0);
int priceNewpath = node.val + leftGain + rightGain;
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, priceNewpath);
return node.val + Math.max(leftGain, rightGain);
}
}
|
建树
在笔试题中,需要自己根据数组建树。数组的形式不同,有两种建树方式。
-
递归法:三叉树
public static Node buildTree(int[] tree, int idx){
if(tree[idx] == -1){
return null;
}
Node root = new Node(tree[idx]);
if(idx * 3 + 1 < tree.length){
root.left = buildTree(tree, idx * 3 + 1);
}
if(idx * 3 + 2 < tree.length){
root.middle = buildTree(tree, idx * 3 + 2);
}
if(idx * 3 + 3 < tree.length){
root.right = buildTree(tree, idx * 3 + 3);
}
return root;
}
|
该方法需要数组非常的完整,对于null节点的左右节点,仍然需要在数组中用null表示,否则数组长度不够会导致建的树不完整。
-
层序遍历
public static Node buildTree(int[] nums){
Node root = new Node(nums[0]);
Queue<Node> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(root);
int idx = 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty() && idx < nums.length){
int size = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
Node node = queue.peek();
queue.poll();
if(idx < nums.length && nums[idx] != -1){
node.left = new Node(nums[idx]);
queue.offer(node.left);
}else{
node.left = null;
}
idx++;
if(idx < nums.length && nums[idx] != -1){
node.middle = new Node(nums[idx]);
queue.offer(node.middle);
}else{
node.middle = null;
}
idx++;
if(idx < nums.length && nums[idx] != -1){
node.right = new Node(nums[idx]);
queue.offer(node.right);
}else{
node.right = null;
}
idx++;
}
}
return root;
}
|
该方法的数组不需要将null节点的子节点表示出来。
三叉树的最大路径和
对于笔试题的三叉树,只需将上两步融合。
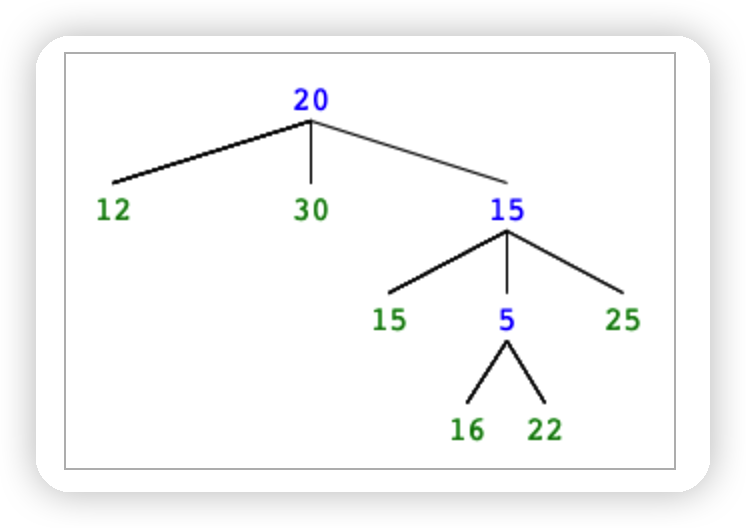
输入:
19
20 12 30 15 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 15 5 25 -1 -1 -1 16 -1 22
其中,-1表示空节点
输出:
92
|
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
class Node{
int val;
Node left;
Node middle;
Node right;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] tree = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
tree[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
Node root = buildTree(tree);
maxGain(root);
System.out.println(maxSum);
}
public static int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public static int maxGain(Node node){
if(node == null){
return 0;
}
int leftGain = Math.max(maxGain(node.left), 0);
int middleGain = Math.max(maxGain(node.middle), 0);
int rightGain = Math.max(maxGain(node.right), 0);
int price = node.val + Math.max(leftGain + middleGain, Math.max(middleGain + rightGain, leftGain + rightGain));
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, price);
return node.val + Math.max(Math.max(leftGain, middleGain), rightGain);
}
public static Node buildTree(int[] nums){
Node root = new Node(nums[0]);
Queue<Node> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(root);
int idx = 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty() && idx < nums.length){
int size = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
Node node = queue.peek();
queue.poll();
if(idx < nums.length && nums[idx] != -1){
node.left = new Node(nums[idx]);
queue.offer(node.left);
}else{
node.left = null;
}
idx++;
if(idx < nums.length && nums[idx] != -1){
node.middle = new Node(nums[idx]);
queue.offer(node.middle);
}else{
node.middle = null;
}
idx++;
if(idx < nums.length && nums[idx] != -1){
node.right = new Node(nums[idx]);
queue.offer(node.right);
}else{
node.right = null;
}
idx++;
}
}
return root;
}
}
|
参考
LeetCode官方题解
jiankychen教你学算法 - 学算法,看我就够了


